Meet Adiquit: Your Clinically Proven Quit-Smoking Pocket Therapist
Adiquit, a member of StartupYard Batch 9, has a singular mission. To help smokers quit, and stay cigarette free. Unlike most apps or quit-smoking programs that smokers may have experienced, AdiQuit is unique in that it is the product of a team of industry leading tobacco addiction researchers and clinical therapists.
Together they’ve pooled their combined experience into a smoking cessation app and online platform that acts as an interactive therapist for smokers. The Adiquit app, which will premiere in Czechia in September 2018, will guide smokers through the quitting process, with constant communication between the app and the smoker, based on clinically proven smoking cessation techniques.
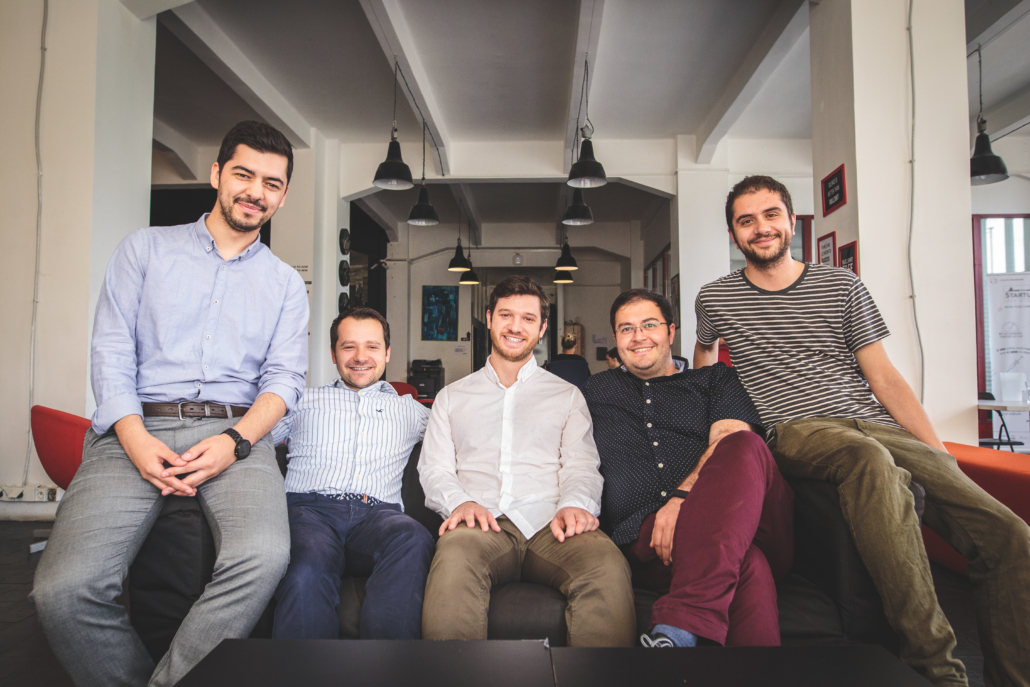
I sat down with Adiquit Co-Founder, psychotherapist and addiction scientist Roman Gabrhelik to talk about the team of academics behind the project, about addiction, and about their program. Here’s what we talked about:

Hi Roman, first tell us a bit about the team, and how you ended up founding AdiQuit together.
Today we’re 3 co-founders, but the whole thing started many years ago- not as a startup. Daniel Novak and I were trying to get funding for an academic research project. We were planning to evaluate the efficacy of smoking cessation programs with our Norwegian partner Håvar. Adam Kulhanek joined us about 2 years ago.
Anyway, we were until recently a really typical “academic team.” We wrote lots of grant proposals, and secured just enough funding to allow us to keep the therapeutic program for smoking cessation running.

We have written many grant proposals to get enough funding that would allow us to develop the smoking cessation therapeutic program further. A couple of months ago we got sick and tired of writing grant applications over and over again, and were offered to take part in the Laborator Nadace Vodafone.
They connected us with you guys and we joined Batch 9 at StartupYard. Daniel, Adam and I are the founders, and we have a team of 9, focused on creating a smart assistant to help smokers quit for good, using our depth of experience and clinical research, along with data we can only get from daily interaction with our users via our app and online platform.
Your team is mainly academic in background. How has it been transitioning into a technology startup, for better or worse?
Yes, it is a different world. The academic background, I guess, is something that makes us different from some of the projects in SY, though not all. This may be our advantage to some degree that we somehow are sticking out. Many startups have to learn their market first, whereas we come with a base of knowledge about smoking cessation therapy.
At the same time many things are new to us and we must learn quickly along the way. For example: how to talk about the product and make it attractive to users, how to do financial projections, how to convince someone to support us, etc.
The stakeholders involved in a venture backed tech company are very different in mentality and experience. That is a challenge for us, because research and learning alone can’t justify our activities as in academia. On the other hand it’s a welcome change, because it forces us to prioritize getting a solution to our customers and getting results quickly.
In an academic project, you take much more time to analyze and think about the data. Here we are learning to make assumptions more quickly, and move in the direction where we gain traction, not necessarily always where we imagined ourselves.
There are seemingly thousands of smoking and tobacco use reduction methods and programs. What makes AdiQuit unique among all of them? Where do most of these systems fail?

Smoking Cessation is a Multi-Billion Dollar Industry
Tobacco dependence is one of the strongest and most pervasive addictions. Most people know this, and it’s evident just walking down the street in any city. It is a major public health issue, with enormous costs to society and the economy. So of course there are many competing solutions to that problem, coming from many angles, such as self-help books, support groups, nicotine replacement, and even hypnosis.
What makes AdiQuit special is our ability to truly personalize treatment; to go beyond a motivational or organizational tool (as many apps and books are), and work to modify a smoker’s actual behavior on a daily basis. AdiQuit has the knowledge of a clinically experienced therapist, but with 24/7 availability, and is focused on preventing relapses in smoking.
Just as a therapist would be able to observe a patient and intervene when they spot behaviors or triggers that will cause the patient to relapse, AdiQuit can do this by maintaining constant communication with the user. In future, we can extend AdiQuit’s reach to smart devices that track user’s physical symptoms, so that we can predict and thus prevent triggers from even happening, using clinically proven diversion techniques.
For any smoker out there who has quit before, you will know exactly what this means. Imagine that your smartphone could tell you, before you even got a chance to smoke, that you were in danger of relapsing, and give you the tools to stop it ever happening.
As we say, quitting smoking is not that hard, which is why many smokers have quit many times, for months or even years. What is hard is actually never to smoke again. Smoke one cigarrete, and many smokers feel that they have already failed to quit. Many approaches to quitting focus on the stopping part, but the “holding on” part is where most quitters fail. For that you need a constant support mechanism, that stops “just one cigarette,” from causing a complete relapse.
In a bit more detail, what will a smoker’s experience be with using AdiQuit, from the first day of using the app, to whenever they have successfully quit?
The smoker can view AdiQuit as a therapist in their pocket, a quitting mate, or an ally that guides her/him through the most difficult period of time without cigarettes.
AdiQuit and the smoker are in dialogue-like contact on a daily basis, throughout the day. In the first phase, the AdiQuit helps the smoker to get ready for his/her first day without a cigarette. From the first day of not smoking AdiQuit makes constant checks and provides all kinds of information and skills in the right time and settings.
Your personal therapist knows that you are most tempted in the morning after a coffee, or after lunch, or maybe in the hour after you leave work, or when you are waiting for the bus. Having already gathered this data from the user during the pre-quitting process, AdiQuit now has the knowledge about you to know when you are vulnerable, and help you in that moment.
Smoking is ritualistic. When Europeans first encountered tobacco in use by Native Americans, it was a ritualistic herb said to contain special powers. Since then, it has maintained this ritualistic place in the lives of those who smoke it. Smokers who quit can feel a sense of loss, as if losing a friend, because the ritual of smoking is a big part of their self-identity.
The good thing about this is that once we understand how smoking fits into someone’s life, we can begin to separate it out and eliminate it. A person’s identity can be changed, just a little at a time, until they are free from cigarettes.
The consumer facing app that AdiQuit will sell on app stores will be quite expensive – up to €100 or more. What is the reasoning behind this approach?
Great question. I think it will be easy for some to say that we are being greedy, charging so much for a way to quit smoking.
However, there’s a deeper motivation here, and it has to do with user psychology. In order to really work as intended, AdiQuit needs to be taken very seriously by its users. They must interact with the app, they must be consistent, and responsive when the app tells them to do something or read something.
We know from our experience as practicing psychologists and researchers that if a person takes a decision in which they invest a significant amount of money, they are much more likely to value and to try and gain from that investment. If your pen costs €1, you may lose it within a day, and not be disturbed. But if your pen costs €100 euros, you’re going to be much more careful with it, and probably you won’t lose it.
The same logic applies to quitting. The truth is that therapeutic treatments and other literature can also be equally or even more expensive. In private practice, a patient would pay me much more to help them through the quitting process. However the act of paying is part of the therapy in this case: it is a sign of commitment, and it is a kind of barrier between those who are not serious enough, and those who are truly motivated to quit.
There will also be an enterprise version of the app that can be used by large organizations as a health benefit to their employees. In this case, employees may not invest money directly in the program, but again, there will be strong reward mechanisms for continuing to do the treatment and sticking with the whole process. That may also include monetary motivation, either as cash or as gift cards, coupons, and other cash-like rewards.
This topic remains an open question for our team. We will evolve according to experience of what ends up working best for our users. The object is to successful help as many people as we can to quit smoking permanently. How we balance that with our business model will be something we have to learn over the coming months.
Smoking rates are falling in Western countries. How do you plan to grow the business into the future? WIll you focus on new markets with more smokers, or transition to treating other types of addiction?
It is a great thing if we run out of opportunities to help smokers quit. We will have won!
This is why we actually started this – to help people quit smoking, which has literally no health benefits to smokers. Unfortunately we are far from having no smokers to use AdiQuit. And if we are overly successful in helping people quit, there are way too many addictions and health problems we can focus on instead.
Our mid-term vision also includes alcohol abuse treatment. The truth is that human beings are prone to addictions, and this fact is not going to change just because of cultural shifts. One or another drug or addictive behavior has cycles of popularity or widespread acceptance, and then may recede, only to rise again later on somewhere else. We see this also with smoking: the West may be smoking less, but Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa are smoking more.
I’m afraid despite our efforts, it will be generations before smoking ceases to be a public health crisis.
You joined StartupYard after taking part in the Vodafone Foundation startup program. How has the experience met up with your expectations? What have been the biggest challenges for your team so far?
It is like a ride on a roller coaster. I guess we are in the middle of it. It is full of adrenalin, the speed is tremendous, and it`s hard to predict if the next curve is going left or right (e.g., from where and when new opportunities occur). But speaking on behalf of the team: we enjoy it very much. Even though it is quite demanding.
If there is a smoker reading this, would there be one thing you’d want them to know? How and when can people get their hands on AdiQuit and start using it?
Yes, there are actually two things:
1) Every day of not smoking matters – we want to help smokers to quit but even taking a break from smoking for some time (even weeks) makes the smoker experience something new. For us the important message to smokers is that accidents often happen, but the trip can still be finished.
2) You are not alone if you are ready to quit smoking – AdiQuit is here to provide help and support. We can do this together.
The official release of AdiQuit for ordinary smokers is planned for September 2018. Those interested can go to the website now, and sign up to become our first users.
Also Check out AdiQuit in the Press: